Why geography is important- Skills That Go Beyond The Map. Plus Resources!
The importance of geography is often overlooked but the subject offers lots of skills that benefit students in their everyday lives.
Geography is often considered a ‘marmite’ subject. You either love it or hate it. Yet in recent years it has enjoyed a surge in GCSE and A Level students studying geography– with over 100,000 more entries in the last 10 years alongside an increase in students going on to complete a geography degree.
This blog explains why geography is important and how it can benefit your students far beyond reading a map.
11 Benefits of Studying Geography
When students study geography, they learn about global matters that will be as relevant for the rest of their lives as they are today. Which is a great foundation for those pursuing a geography degree but also helps to develop a range of transferable skills all students will use throughout their lives.
Here are the main benefits of studying geography:
Develops an appreciation for the planet
Geography is the only subject to provide a broad view of the world and how it functions.
This is important because it allows us to build a deeper understanding of the world we live in, the natural environment and human landscapes and all the connections between them. This understanding can empower students (and teachers!) to be more responsible when it comes to climate change.
Benefits for students
- Develops an understanding of physical properties and processes that shape our landscape
- Builds an awareness of the differences of human geography and physical landscapes that shape our societies, cultures, economies and politics
- Develops an appreciation for the world around us

Resource recommendation
Develops an awareness and understanding of different cultures
Human geography teaches students about different cultures’, beliefs, customs, languages and traditions. When studying geography, students learn about how different people live around the world which, this helps develop an appreciation and understanding for many cultures different to their own.
Benefits for students
- Cultural geography encourages an outward-looking global perspective
- Empowers students to be more informed about many cultures
- Develops cultural sensitivity towards cultural issues
Resource recommendation
KS3 ‘Who Do We Think We Are?’ by the Royal Geographical Society
Encourages critical thinking
The wide range of topics studied in geography (and the complex interaction between them) helps develop critical thinking because students will analyse a variety of different viewpoints. This is an important life skill because it encourages students to look at different perspectives and challenge data and evidence.
Benefits to students
- Trains students to consider differing viewpoints which helps develop an appreciation of people’s differing opinions
- Discussing contrasting views helps students develop communication skills
- Enhances important transferable skills for the future like problem-solving and decision-making

Resource recommendation
GeogPod podcast by The Geography Association- Episode #0: ‘Rebecca Kitchen: Critical Thinking for Achievement’
Builds mathematical and analytical skills
Both physical and human geography study involve collecting data and analysing evidence to make conclusions.
For example, while studying natural hazards, you may collect data on the frequency of hazards compared to the relative wealth of a nation and the death toll of the hazard. This requires collecting and comparing mathematical data, analysing the information and making conclusions from the evidence.
The evidence-based scientific approach develops core skills like numeracy and graphicacy (the ability to understand and use a map or graph).
Benefits to students
- Develops mathematical skills which can be transferred to lots of future job roles and everyday life
- Develops analytical skills that support their other subjects like English and History
Recommended resource
Geography Pods ‘factfulness’ resources
Develops knowledge of global crisis issues
In an era when environmental degradation such as climate change, deforestation, habitat destruction, natural disasters and biodiversity loss are becoming increasingly critical, geography has a key role in helping students understand our planet.
By its holistic nature, geography helps us understand the Earth’s natural environmental systems and processes, consider the impact of human activities on them, and evaluate the environmental consequences.
Studying environmental degradation highlights the importance of our planet and encourages students to want to protect it.
Benefits to students
- Introduces students to global issues and environmental degradation
- Helps develop a sense of responsibility for our planet
- Builds an awareness of sustainability, conservation, adaptation and mitigation

Recommended resource
Geography all the way: Climate and Vegetation
Develops problem solving skills
One of the main ways geography differs from other subjects is that it doesn’t aim to simply tell students about issues, but to provide them with opportunities to consider the solutions as well. Therefore, when studying geography, students use their problem-solving and decision making skills often.
For example, if students are studying coastal floods, they will evaluate data about the flood risks before assessing potential solutions. This process forces them to weigh up different options before making an informed decision.
In todays world, transferable skills like problem solving skills are essential for lots of future job roles as well as everyday life.
Benefits to students
- Become more empowered to consider various solutions to their problems
- Helps develop research and enquiry skills including data collection, analysis and interpretation
- Enables better decision-making skills and their ability to communicate their decisions
Recommended resource
BBC Bitesize ‘Planet Planners’ game: includes flooding, urbanisation and hazards for KS3
Improves Literacy and Communication Skills
Geography is a literacy-based subject that incorporates reading, comprehension, interpreting information, and sharing findings through written and verbal communication.
Good communication is critical for collaborating with others and sharing ideas which is one of the major ways geography helps students in other areas of their lives.
Benefits to students
- Develops crucial communication skills beneficial to future employment
- Supports better understanding of text and literacy in other subjects
- Builds complex vocabulary

Recommended resource
Discover The World Education- Coasts Assessments MATS
Develops knowledge of globalisation and trade
Countries throughout the world communicate, share their cultures and goods through travel and trade. Nowadays, improved communication means that this can happen quickly, however when something happens in one area of the world, it can have a domino effect worldwide. Also known as globalisation.
Geography helps us navigate the complexities of global trade, diplomacy and cultural exchange which is essential for businesses. A knowledge of globalisation helps students understand the distribution of wealth and resources as well as important global issues like poverty, economic planning, policy-making and inequality.
Benefits to students
- Develops conflict resolution skills
- Teaches the principles of sustainability to help students make responsible choices
- Informs students as future citizens about international relations
Recommended resource
The Geographical Association ‘Switched on or switched off’
Develops spatial awareness
Studying geography helps students to develop a sense of place and space, and spatial awareness which helps them navigate the world and their place within it.
Geography students use spatial analysis if they’re organising an urban space, planning risk zones to hazards or interpreting relationships between different places. These skills help students in their everyday life whether they need to read a map, use a satnav or choose a route to get to work.
Benefits to students
- Helps students understand spatial data, spatial distribution and spatial analysis through technology
- Enhances fieldwork and outdoor learning observation skills
- Acquire cartographic and data visualisation skills

Recommended Resource
Geography Education Online: Geographical skills and enquiry resources
Improves understanding of global disease & hazards
It has become increasingly relevant to have a good understanding of the geographic spread of diseases and global hazards, particularly living post Covid.
This information and the geographic pattern of risk is crucial for improving how we can be prepared for future hazards.
Studying geography helps us understand:
How to assess and monitor risk of natural hazards
How to mitigate disasters such as earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, floods, etc.
How natural hazards are spread across the world
How diseases can be tracked
How access to healthcare varies
How public health officials make decisions in healthcare planning
This information and the geographic pattern of risk is crucial for improving how we can be prepared for future hazards.
Benefits to students
- Better understanding of global patterns of risk
- Employable skills for example in healthcare and disaster planning
- Improved skills in planning and preparation
Resource recommendation
Discover The World Education: Fagradalsfjall Tectonic Hazards pack
Offers outdoor learning
Geography offers lots of opportunities for students to explore outdoors through fieldwork. For example, students studying erosional landscapes may visit a local coastal town or pupils learning about renewable energy could visit the Krafla geothermal power station in Iceland. Whether you stay local or go further afield, nothing brings geography to life more than seeing the processes come to life in the real world.
Learning outdoors has many benefits. Like allowing students to explore geographical processes that form various environments and how this transforms them over time. This will develop their knowledge through observing, mapping, measuring and recording which creates a deeper understanding.
Benefits to students
- Explore geographical processes that create and transform environments
- Use different geographical tools to help their interpretation and decision-making
- Communicate geographical knowledge based on their own experiences

In summary, geography is not just an academic interest. It is an essential subject for navigating modern life and making sense of our world. Geography empowers students to become better informed citizens with well-rounded, adaptable and active skills.
What is geography?
This is the classic university or teacher training question, and it’s surprisingly tricky to answer!
In simple terms, it’s the study of the Earth and its components. But when studying geography, we are not just studying the physical world, but also the people, cultures, politics and human history that have shaped the human world too.
Generally speaking, we divide geography up into three categories: physical (the natural world and its processes), environmental (how humans impact the Earth) and human geography (how people interact in a place).
These categories are inextricably linked, with each having an influence on the other. Geography aims to bring these together to consider our world in a more holistic manner.
Some argue that this generalisation can dilute a subject. But actually it’s a unique bridge between social and natural sciences.
Human Geography
The Royal Geographical Society defines human geography as “the study of the dynamics of the people and cultures of the world, your place within the world and your identity and how this links to place and space.”
It considers:
- Socio-economic links
- Population
- Migration
- Urban change and urban geography
- Globalisation
- Political geography
- History
- Other cultures
Human geography considers what makes us similar and different, and the causes of inequalities between places and social groups. For example, we might study how human health and life expectancy varies at a local, regional, national and global level.
Physical Geography
Physical geography considers how landscapes are created and change over time. While it involves the study of processes that shape our physical landscapes and environments, it sets this within the context of how people also have an influence on these natural processes.
For example, we can be studying the natural processes of how rivers flow and shape the land, but set this within the context of how this has an impact on people and society and how in turn people have an influence on these processes themselves.
This includes looking at:
- Rivers
- Coasts
- Glaciers
- Uplands and lowlands
- Habitats
- Oceans
- Weather and climate
- Biomes and ecosystems
- Natural hazards
- Atmospheric and oceanic circulation
Environmental Geography
Environmental geography studies the interactions between the humans and their natural environment (including the outcomes of these interactions).
Environmental geography is essential when studying themes like natural resources, habitats, or climate change and how they influence each other.
You can imagine environmental, physical and human geography as being part of an interlinked Venn diagram:
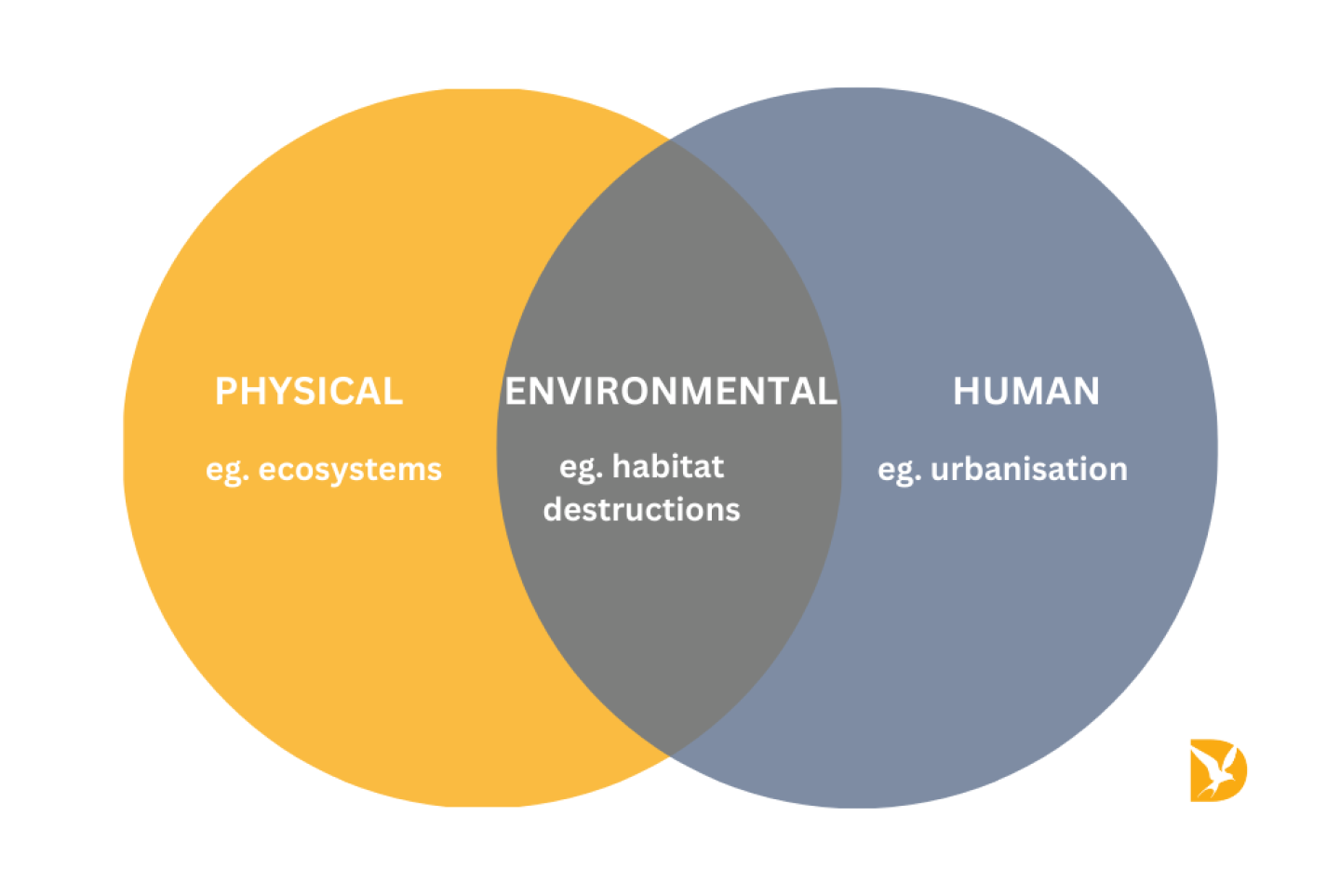
FAQs
What are the different types of geography? There are 3 types of geography: physical geography, human geography, and environmental geography which combines the 2.
What are the benefits of studying geography? Geography empowers students to become better informed about our world, with transferable skills suitable for a range of jobs.
What transferable skills does geography offer? Geography students develop excellent numeracy and literacy skills, data collection and analysis, oral and written communication, and problem-solving.



